The Ultimate Guide to Lithium-ion Battery Storage
Lithium-ion batteries pose a fire hazard, so proper storage is essential.
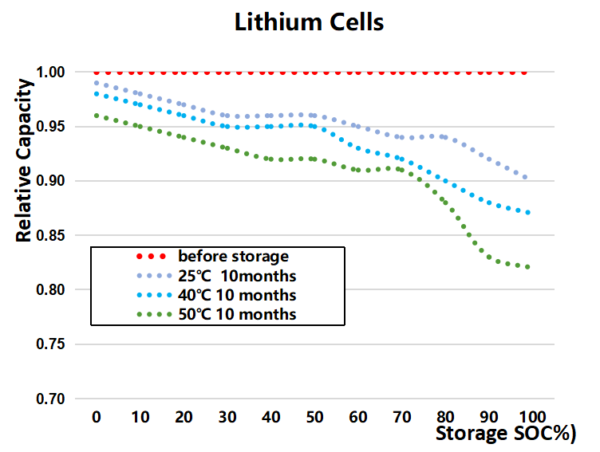
For optimal storage, lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries should neither be stored fully charged nor completely discharged. The best approach, backed by extensive research, is to store them at 40-50% capacity in a cool environment, ideally between 5°C and 15°C, but not below 0°C. Since Li-ion batteries self-discharge, it’s advisable to recharge them every 12 months.
Short-term storage: Store the battery in a dry, non-corrosive environment at temperatures between -20°C and 35°C. Extreme temperatures may cause rusting of metal parts or battery leakage.
Long-term storage: Long-term storage can cause battery passivation and increase self-discharge. To counter this, store the battery at 10°C-30°C and perform a charge/discharge cycle every 3 months to maintain its activity and performance.
Charge the battery to 40-50% and store it in a cool, dry environment. While cooler temperatures and a partial charge extend battery life, avoid letting the charge drop too low, as self-discharge over time can severely shorten battery lifespan.
The storage temperature has a direct impact on the permanent capacity loss of the battery.
| Storage Temperature (℃) | 40% State of Charge(SOC) | 100% State of Charge(SOC) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 38%(one year later) | 94%(one year later) |
| 25 | 36%(one year later) | 80%(one year later) |
| 40 | 32%(one year later) | 65%(one year later) |
| 50 | 25%(one year later) | 60%(one year later) |
Should You Remove the Battery from a Device During Prolonged Inactivity?
Yes, it’s important to remove the battery from a device during prolonged inactivity. Even when switched off, a small current can flow through the device, leading to complete discharge and potential battery damage, or worse, harm to the device itself.
Here are important prohibitions to follow for lithium battery storage:
- Avoid charging or storing the battery in extreme heat or near fire.
- Stop using the battery if it swells or leaks.
- Keep the battery away from water.
- Never throw the battery into fire or expose it to heat.
- Do not plug the battery directly into a power outlet or car cigarette lighter.
- Avoid short-circuiting the battery by contacting its terminals with metal objects.
- Prevent impacts, punctures, or modifications, and avoid exposing the battery to direct sunlight or microwaves.
- Do not hit, throw, or subject the battery to mechanical shock.
- Use only approved lithium battery chargers, not inferior or incompatible ones.
- Never disassemble the battery.
- Avoid storing or mixing the battery with metal objects.
- Don’t mix different types, models, or capacities of batteries.
- Discontinue use if the battery emits unusual odors, heat, or shows signs of deformation or discoloration.
- Ensure batteries are protected from moisture, crushing, or impact during transport.
- Do not use or store the battery in high-temperature environments, such as hot cars or direct sunlight.
- Keep the battery away from strong static electricity or magnetic fields.
- Immediately stop use if the battery shows any signs of abnormality during use, storage, or charging.
- Cover discarded batteries with insulating paper to prevent fire or explosion.
Lithium Battery Storage Checklist
1. Remove the battery from the device before storage.
2. Charge or discharge the battery to 3.8V (use a charger with a “storage mode” or a voltmeter to check the voltage).
3. Protect the battery terminals with insulating material (e.g., plastic or electrical tape).
4. Store the battery in a fireproof bag or container.
5. Designate a specific “Lithium-ion battery only” storage area.
6. Ensure the storage location is at room temperature and away from heat sources.
7. Keep the area dry and well-ventilated.
8. To enhance safety, remove any flammable materials (e.g., wood, carpet, gasoline) and consider using ceramic or cement surfaces.
9. Keep an ABC or water fire extinguisher nearby, and be familiar with its location.
Factory storage measures
1. The cell or battery storage areas should be set up independently.
Put up conspicuous signs at the storage places with the inscription “Fireworks prohibited”. It is strictly forbidden to stack flammable and combustible objects nearby.
2. The temperature of cell or battery storage should be controlled within a range of 20±5℃,
The maximum should not exceed 30℃,
The relative humidity should not be higher than 75%.
Keep the storage clean, dry and well ventilated, and do not store other items.
3) Cell or battery storage should be equipped with smoke and temperature alarm devices, and the alarm signal should be transmitted to a place where someone is on duty 24 hours a day.
4) Cell or battery storage facilities should be equipped with independent external accident extraction devices.
Accident extraction devices should be interlocked with smoke and temperature alarm devices.
5) Cells and batteries should be stored neatly and not stacked too high, and storage facilities should be made of non-combustible material and antistatic measures should be taken.
6) The positive or negative terminal of each battery (cell) should be insulated to prevent short circuit protection measures.
7) Automatic sprinkler systems shall be installed in the battery storage area.
8) Battery shall not be stored at full capacity, it is recommended to store at 50% capacity.
9) Semi-finished batteries should be provided with protective plates.
10) Waste batteries should be stored separately after they are discharged.
11. Each fire safe zone of battery and cell storage should not exceed 250 square meters.
12. Battery and cell storage should have a sufficient number of spherical automatic dry powder fire extinguishers or sprinklers.
13.The battery and cell stores should be equipped with 2 fire blankets each and a special bucket for handling accidental batteries.
PS:
1. Explosion-proof electrical equipment should be used in battery storage and aging rooms.
2. Defective batteries and spent batteries must be placed in special treatment cabinets for isolation and disposal, and the use of explosion-proof sand buckets for handling accidental batteries is recommended.
Storage measures for daily lithium battery users
Battery storage areas should be set up independently with clear signs stating “Fireworks Prohibited.” It is strictly forbidden to store flammable or combustible objects nearby.
The storage temperature for batteries should be maintained at 20±5℃, not exceeding 30℃, with a relative humidity below 75%. Keep the area clean, dry, and well-ventilated, with no other items stored in the space.
Storage areas should be equipped with smoke and temperature alarms, with signals sent to a 24-hour monitoring location.
Battery storage facilities should have independent external accident extraction systems, interlocked with smoke and temperature alarms.
Batteries should be stored neatly without stacking too high, and storage facilities should be made from non-combustible materials with antistatic measures.
Ensure the insulation of battery terminals to prevent short circuits.
Install automatic sprinkler systems in battery storage areas.
Batteries should not be stored at full capacity—50% charge is recommended.
Semi-finished batteries should have protective plates.
Waste batteries should be stored separately after being discharged.
Each fire-safe zone for battery storage should not exceed 250 square meters.
Battery storage areas should be equipped with spherical automatic dry powder fire extinguishers or sprinklers.
Ensure the availability of two fire blankets and a special bucket for handling accidental batteries in storage areas.
Additional Notes:
- Use explosion-proof electrical equipment in battery storage and aging rooms.
- Defective and spent batteries should be placed in special treatment cabinets for isolation. Use explosion-proof sand buckets to handle accidental batteries.
FAQ on lithium battery storage
Studies have shown that lithium-ion batteries can experience a charge loss of 3 to 5 percent per month due to self-discharge, which depends on factors like temperature, battery power, and design. Higher temperatures generally increase self-discharge.
When a battery is fully discharged, its voltage drops to 0 volts, and if left in this state, a chemical reaction between the electrodes can occur, making the battery partially or completely unusable. This significantly reduces its capacity and prevents recharging. Therefore, it’s important not to discharge a lithium-ion or lithium-polymer battery below its type-specific final voltage, and it should be recharged as soon as possible. Ideally, these batteries should be recharged when they reach 10 to 20 percent of their remaining capacity. Most high-quality lithium-ion batteries include protection circuitry to prevent over-discharge, overcharge, and explosion.
Recommended Temperature Range for Use:
Lithium-ion batteries can operate between -20°C and +55°C, but charging should only occur between 0°C and 45°C.
Battery Life:
Under optimal conditions, lithium-ion batteries can last up to 1,000 charge cycles. However, this varies depending on capacity and how the battery is used. Over time, the battery’s capacity decreases, and it is generally considered “worn out” when its capacity falls below 70% of its rated value.
Memory Effect and Lazy Battery Effect:
The “memory effect,” associated with older NiCd batteries, occurs when a battery “remembers” how much it was used and reduces its charge capacity if not fully discharged. Similarly, NiMH batteries experience a “lazy battery effect.” In contrast, lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries have no memory effect and can be charged at any time without concern. These batteries should not be fully discharged, and it is recommended to recharge them when they still have 10 to 20% capacity. Fully charging and reconnecting a battery won’t increase its charge and can negatively affect performance.









Add comment